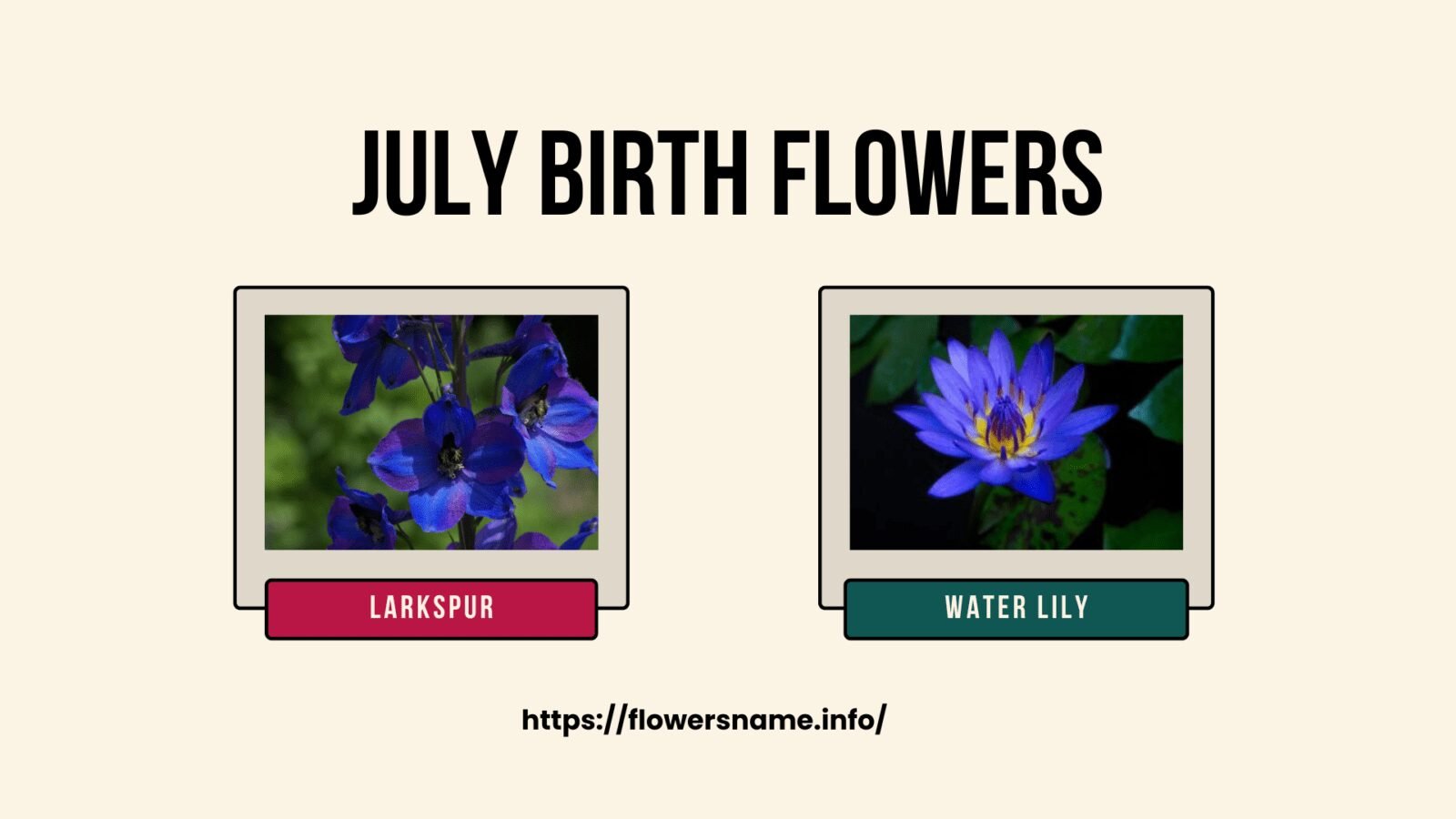
The July Birth flower is the Larkspur and the Water Lily.
Larkspur, also known as Delphinium, is a tall and elegant flower that comes in a variety of colors such as purple, blue, pink, white, and red. It symbolizes lightness, levity, and swiftness, making it a great flower to represent July, which is a month associated with sunny days, leisure, and joy.
Water Lily, on the other hand, is an aquatic flower that grows in calm freshwater environments such as ponds and lakes. It has a unique beauty and tranquility and is often associated with enlightenment, rebirth, and purity. The Water Lily is also believed to represent the 13th wedding anniversary.
Both flowers have their own meanings and beauty, making them a perfect choice for representing the month of July.
July Birth Flower – Larkspur
Larkspur, also known as Consolida ajacis or Delphinium ajacis, is a flowering plant that belongs to the family Ranunculaceae. This herbaceous annual is native to the Mediterranean region but is now widely cultivated all over the world as an ornamental garden plant. Larkspur is known for its tall, elegant spikes of flowers that bloom in a range of colors, including blue, pink, purple, white, and red.
Description and Characteristics
 Larkspur plants can grow up to 3 feet tall and have feathery, fern-like foliage that is deeply divided into numerous segments. The plant produces dense spikes of flowers that emerge from the upper portions of the stems. The flowers are single or double, with five petals that are elongated and pointed, resembling the shape of a spur. The flower spikes are typically 6-12 inches long and can contain dozens of individual flowers.
Larkspur plants can grow up to 3 feet tall and have feathery, fern-like foliage that is deeply divided into numerous segments. The plant produces dense spikes of flowers that emerge from the upper portions of the stems. The flowers are single or double, with five petals that are elongated and pointed, resembling the shape of a spur. The flower spikes are typically 6-12 inches long and can contain dozens of individual flowers.
Larkspur blooms in late spring or early summer and lasts for about four to six weeks. The plant prefers full sun but can tolerate partial shade. It thrives in well-drained soil that is rich in organic matter. Larkspur requires regular watering, especially during hot and dry weather.
Related: August Birth Flower
Uses and Benefits
Larkspur is primarily grown as an ornamental garden plant for its attractive flowers. It is often used in borders, cottage gardens, and wildflower meadows. Larkspur is also popular in cut flower arrangements due to its long stems and striking flowers.
Apart from its aesthetic value, larkspur has some medicinal uses. The plant contains various alkaloids, including delphinine, which has analgesic and sedative properties. It has been used in traditional medicine to relieve pain, reduce fever, and induce sleep. However, the use of larkspur for medicinal purposes should be done with caution, as it can be toxic if consumed in large amounts.
Cultivation and Propagation
Larkspur is relatively easy to grow from seeds. The seeds should be sown directly into the soil in the fall or early spring, as the plant requires a period of cold stratification to germinate. The seeds should be planted about 1/4 inch deep and spaced 12-18 inches apart. Larkspur can also be propagated through division or cuttings.
To ensure healthy growth, larkspur should be grown in well-drained soil that is kept consistently moist. The plant should be fertilized regularly with a balanced fertilizer. Larkspur may need staking to support its tall stems, especially in areas with strong winds.
Pests and Diseases
Larkspur is generally resistant to pests and diseases. However, it can be susceptible to fungal infections, such as powdery mildew and leaf spot, if the plant is grown in conditions that are too damp. To prevent fungal infections, it is important to avoid overcrowding the plants and to provide good air circulation. Aphids and spider mites may also attack larkspur, but they can be controlled with insecticidal soap or neem oil.
In conclusion, larkspur is a beautiful and easy-to-grow garden plant that adds color and elegance to any landscape. With proper care and maintenance, larkspur can provide years of enjoyment for gardeners and flower enthusiasts alike.
July Birth Flower – Water lilies
Water lilies are beautiful aquatic plants that are known for their unique floating leaves and stunning flowers. They are a type of flowering plant that belongs to the family Nymphaeaceae and are native to many parts of the world, including Asia, Europe, and North America. These plants are widely cultivated for their ornamental value and are often used in water gardens and ponds.
Description and Characteristics
 Water lilies are aquatic plants that are well adapted to living in still or slow-moving water bodies. The plant’s leaves and flowers float on the surface of the water, with the roots anchored in the mud or soil at the bottom of the pond or lake. Water lily leaves are large and circular, ranging in size from a few inches to several feet in diameter. The leaves have a waxy coating that helps them repel water, and they are attached to long stems that allow them to float on the water’s surface.
Water lilies are aquatic plants that are well adapted to living in still or slow-moving water bodies. The plant’s leaves and flowers float on the surface of the water, with the roots anchored in the mud or soil at the bottom of the pond or lake. Water lily leaves are large and circular, ranging in size from a few inches to several feet in diameter. The leaves have a waxy coating that helps them repel water, and they are attached to long stems that allow them to float on the water’s surface.
The flowers of the water lily are the plant’s most striking feature. They are large and showy, with multiple petals arranged in a circular pattern. Water lily flowers come in a range of colors, including white, yellow, pink, and red. The flowers typically bloom in the summer months and remain open for a few days before closing and sinking beneath the water’s surface.
Uses and Benefits
Water lilies are primarily grown for their ornamental value. They are popular additions to water gardens, ponds, and other water features due to their beauty and unique floating leaves. Water lilies also provide shelter and food for aquatic animals such as fish, frogs, and insects.
In addition to their ornamental value, water lilies have some medicinal uses. The plant contains compounds that have been shown to have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial properties. Some traditional medicines use water lily extracts to treat a range of health conditions, including diarrhea, wounds, and respiratory infections.
Cultivation and Propagation
Water lilies are relatively easy to cultivate in a pond or other water feature. The plant requires full sun and still or slow-moving water that is at least 2-3 feet deep. Water lilies prefer nutrient-rich soil, but excessive nutrients can cause algae growth, which can harm the plant. To maintain healthy water lilies, it is important to monitor and balance the water’s nutrient levels.
Water lilies can be propagated by dividing the roots or by collecting seeds. To divide the roots, the plant should be lifted from the water and the roots carefully separated. Each new plant should have at least one leaf and a healthy root system. Water lily seeds can be collected after the flowers have bloomed and should be sown immediately in nutrient-rich soil.
Pests and Diseases
Water lilies are generally resistant to pests and diseases. However, they can be susceptible to fungal infections, such as leaf spot and rust, if the water is too warm or there is poor air circulation. To prevent fungal infections, it is important to keep the water clean and to maintain good water circulation. Some aquatic insects, such as water lily beetles, may also attack the plant, but they can be controlled with insecticidal soap or neem oil.
In conclusion, water lilies are beautiful aquatic plants that are prized for their ornamental value and unique floating leaves. With proper care and maintenance, water lilies can provide years of enjoyment and beauty in water gardens and other aquatic settings.